Table of Contents
Provides an interface for database backup and restore management, scheduling, and reporting. Each backup is assigned with a backup ID and ClusterControl creates a directory under Storage Directory to store the backups based on this ID.
Create Backup
Creates or schedules a MongoDB backup.
Create Backup
Creates a backup of the database immediately. You can choose to create a full backup using mongodump or Percona Backup for MongoDB(PBM). The backup created by this feature will be a full backup.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup Method |
|
| Storage Directory |
|
| Backup Subdirectory |
|
| Upload Backup to the cloud |
|
| Enable Encryption |
|
| Retention |
|
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| B | The date and time when the backup creation was beginning. |
| H | The name of the backup host, the host that created the backup. |
| i | The numerical ID of the cluster. |
| I | The numerical ID of the backup. |
| J | The numerical ID of the job that created the backup. |
| M | The backup method (e.g. “mysqldump”). |
| O | The name of the user who initiated the backup job. |
| S | The name of the storage host, the host that stores the backup files. |
| % | The percent sign itself. Use two percent signs, %% the same way the standard printf() function interprets it as a one percent sign. |
Starting from ClusterControl 1.9.7 (September 2023), ClusterControl GUI v2 is the default frontend graphical user interface (GUI) for ClusterControl. Note that the GUI v1 is considered a feature-freeze product with no future development. All new developments will be happening on ClusterControl GUI v2. See User Guide (GUI v2).
Schedule Backup
Creates backup schedules of the database. You can choose to create a full backup using mongodump or Percona Backup for MongoDB. ClusterControl organizes the backup directory according to the shard or replica set, under the Backup Directory on the ClusterControl host.
The time is the local time on the ClusterControl node.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Schedule |
|
| Backup Method |
|
| Storage Directory |
|
| Backup Subdirectory |
|
| Upload Backup to the cloud |
|
| Enable Encryption |
|
| Retention |
|
| Failover backup if node is down |
|
| Backup Failover Host |
|
If Percona Backup for MongoDB is not enabled, ClusterControl will notify the user to install it first and a shared directory mounted on all MongoDB nodes is required.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| B | The date and time when the backup creation was beginning. |
| H | The name of the backup host, the host that created the backup. |
| i | The numerical ID of the cluster. |
| I | The numerical ID of the backup. |
| J | The numerical ID of the job that created the backup. |
| M | The backup method (e.g. “mysqldump”). |
| O | The name of the user who initiated the backup job. |
| S | The name of the storage host, the host that stores the backup files. |
| % | The percent sign itself. Use two percent signs, %% the same way the standard printf() function interprets it as a one percent sign. |
Scheduled backups
List of scheduled backups. You can enable and disable the schedule by toggling it accordingly. The created schedule can only be deleted and cannot be modified.
Backup Method
This section explains the backup method used by ClusterControl for MongoDB.
A backup process performed by ClusterControl is running on a background thread (RUNNING3) which doesn’t block any other non-backup jobs in the queue. If the backup job takes hours to complete, other non-backup jobs can still run simultaneously via the main thread (RUNNING). You can see the job progress at ClusterControl → Logs → Jobs.
mongodump
ClusterControl uses the standard command to perform mongodump with --journal, which allows mongodump operations to use the durability journal to ensure that the export is in a consistent state against shards.
mongodb consistent
Built on top of Python 2.7, also known as mongodb-consistent-backup, it creates cluster-consistent point-in-time backups of MongoDB via wrapping mongodump. Backups are remotely pulled and outputted onto the host running the tool. Even if you do not run MongoDB 3.2+, it is strongly recommended to use MongoDB 3.2+ binaries due to inline compression and parallelism.
This backup method has been deprecated. You can no longer use this method so please use Percona Backup for MongoDB instead. Any attempt to use this backup method, ClusterControl will raise an error message during the job activity of the backup process.
Percona Backup for MongoDB
Percona Backup for MongoDB is a distributed, low-impact solution for achieving consistent backups of MongoDB sharded clusters and replica sets. Percona Backup for MongoDB supports Percona Server for MongoDB and MongoDB Community v3.6 or higher with MongoDB Replication enabled (standalone is not supported due to the dependency on MongoDB’s oplog). The Percona Backup for MongoDB project inherited from and replaces mongodb-consistent-backup, which is no longer actively developed or supported.
If you have older versions of MongoDB i.e. < 3.6 versions, then your only option to take a backup is mongodump.
Percona Backup for MongoDB requires a remote file server mounted to a local directory. It is the responsibility of the server administrators to guarantee that the same remote directory is mounted at exactly the same local path on all servers in the MongoDB cluster or non-sharded replica set. If the path is accidentally a normal local directory, errors will eventually occur, most likely during a restore attempt.
Backup List
Provides a list of finished backup jobs. The status can be:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| completed | Backup was successfully created and stored in the chosen node. |
| running | The backup process is running. |
| failed | The backup was failed. |
Backup Encryption and Decryption
If the encryption option is enabled for a particular backup, ClusterControl will use OpenSSL to encrypt the backup using the AES-256 CBC algorithm. Encryption happens on the backup node. If you choose to store the backup on the controller node, the backup files are streamed over in encrypted format through socat or netcat.
If compression is enabled, the backup is first compressed and then encrypted resulting in smaller backup sizes. The encryption key will be generated automatically (if not exists) and stored inside the CMON configuration for the particular cluster under backup_encryption_key the option. This key is stored with base64 encoded and should be decoded first before using it as an argument to pass when decrypting the backup. The following command shows how to decode the key:
$ cat /etc/cmon.d/cmon_X.cnf | grep ^backup_encryption_key | cut -d"'" -f2 | base64 -d > keyfile.keyWhere X is the cluster-ID. The above command will read the backup_encryption_key value and decode the value to a binary output. Thus, it is important to redirect the output to a file, as in the example, we redirected the output to keyfile.key. The key file which stores the actual encryption key can be used in the OpenSSL command to decrypt the backup, for example:
$ cat {BACKUPFILE}.aes256 | openssl enc -d -aes-256-cbc -pass file:/path/to/keyfile.key > backup_file.gzOr, you can pass the stdin to the respective restore command chain, for example:
$ cat cat {BACKUPFILE}.aes256 | openssl enc -d -aes-256-cbc -pass file:/path/to/keyfile.key | /usr/bin/mongorestore --host localhost --port 27017 --username backupuser --password mysecret --authenticationDatabase admin --drop --oplogReplay --gzip --archiveSettings
Upon clicking the Settings tab button, two options you can choose are Backup Settings and Percona Backup.
Backup Settings
Manages the backup settings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Default backup directory |
|
| Backup retention period |
|
| Backup cloud retention period |
|
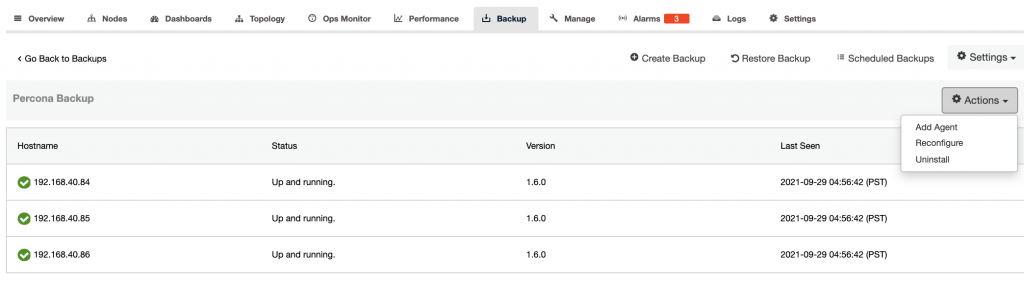
Percona Backup
Manages the Percona Backup for MongoDB (PBM) installation and configuration.
Clicking on the “Actions” button will list down all the possible functionalities.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Add Agent |
|
| Reconfigure |
|
| Uninstall |
|
The dashboard displays the Hostname, Status of the pbm-agent (the backup agent that was deployed and running in your MongoDB nodes), Version of the PBM installed, and Last Seen when it was running.